Introduction
The Zantac lawsuit is one of the most significant legal actions in recent pharmaceutical history, involving thousands of plaintiffs who allege that the popular heartburn medication, Zantac, led to severe health complications, including cancer. This blog delves into the background of the Zantac lawsuit, the discovery of its contamination with a probable human carcinogen, and the legal and health implications for those affected.
Table of Contents

Overview of the Zantac Lawsuit
The Zantac lawsuit emerged after the discovery that the medication, which contains ranitidine, could form N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a potent carcinogen, under certain conditions. NDMA is known to increase the risk of several types of cancer, leading to widespread recalls and thousands of lawsuits against manufacturers like Sanofi and Pfizer. The Zantac lawsuit seeks to hold these companies accountable for failing to warn consumers about the potential dangers of their product.
Background on Ranitidine and NDMA Contamination
Ranitidine, the active ingredient in Zantac, was originally hailed as a breakthrough in treating heartburn and acid reflux. However, studies revealed that ranitidine could degrade and form NDMA, especially when exposed to heat or stored for long periods. NDMA is classified as a probable human carcinogen, meaning it could cause cancer in humans. This contamination is at the heart of the Zantac lawsuit, as plaintiffs claim they were unknowingly exposed to a harmful substance.
What Led to the Zantac Lawsuits?
Discovery of NDMA in Zantac
The discovery of NDMA in Zantac was first made public in 2019 when an independent laboratory, Valisure, detected high levels of the carcinogen in the medication. This finding triggered widespread concern, leading to further investigations by regulatory bodies worldwide.
9 RANITIDINE PRODUCTS CONTAINING NDMA
These are the nine (9) most common Zantac products and generic Zantac products containing ranitidine:
- Zantac 150 Tablets
- Zantac 150 Maximum Strength
- Zantac 150 Maximum Strength Cool Mint
- Zantac 75 Tablets
- Wal-Zan 150
- Wal-Zan 75
- Heartburn Relief
- Acid Reducer
- Acid Control
FDA’s Response and Drug Recalls
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warning says NDMA was found at levels between 3,000 to 26,000 times higher than FDA approved standards.
Following Valisure’s findings, the FDA conducted its tests and confirmed the presence of NDMA in Zantac. In response, the FDA issued a series of warnings, and by April 2020, it requested the removal of all Zantac products from the market. This move prompted the filing of numerous Zantac lawsuits, as consumers who had used the drug for years feared they were at risk of developing cancer.
Public Reaction and Legal Actions
The news of NDMA contamination in Zantac sparked outrage among consumers and prompted immediate legal actions. Thousands of Zantac lawsuits were filed, with plaintiffs seeking compensation for medical expenses, pain and suffering, and punitive damages against the drug’s manufacturers. The public’s reaction highlighted the widespread trust in over-the-counter medications and the devastating consequences when that trust is broken.
Health Risks Linked to Zantac
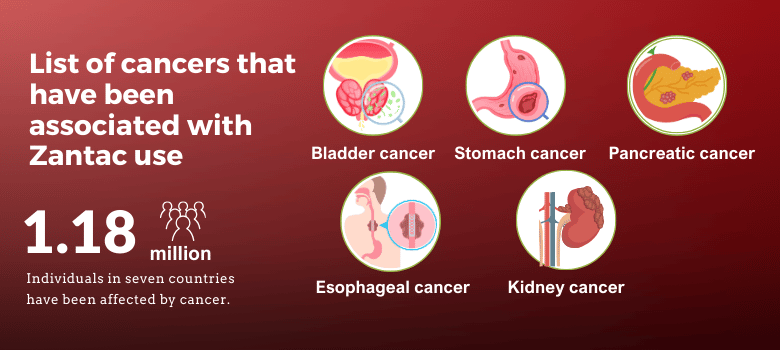
Cancers Associated with Zantac Use
The central claim in the Zantac lawsuit is that the drug’s contamination with NDMA increases the risk of several types of cancer. These include, but are not limited to, bladder cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, and esophageal cancer. Plaintiffs in the Zantac lawsuit argue that they developed these cancers as a direct result of taking the drug.
Other Health Issues: PPH and Crohn’s Disease
In addition to cancer, some plaintiffs have linked Zantac use to other serious health conditions such as Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (PPH) and Crohn’s Disease. While the evidence connecting Zantac to these conditions is less established, they are nonetheless significant issues raised in the Zantac lawsuit.
Scientific Evidence and Medical Studies
Numerous studies have been conducted to explore the link between ranitidine, NDMA, and cancer. While some studies show a strong correlation, others are less conclusive. However, the prevailing scientific consensus acknowledges the potential risks, forming the basis for the Zantac lawsuit. Ongoing research continues to investigate the full extent of these risks.
Notable Zantac Lawsuit Cases
Key Plaintiffs and Their Stories
Several high-profile cases have brought attention to the Zantac lawsuit. These cases often involve plaintiffs who took Zantac for years and later developed cancer. Their stories highlight the personal toll of the drug’s contamination and underscore the importance of holding pharmaceutical companies accountable.
High-Profile Settlements and Dismissals
Some Zantac lawsuits have already resulted in settlements, where companies like Sanofi and Pfizer agreed to compensate plaintiffs without admitting wrongdoing. However, not all cases have led to settlements; some have been dismissed, often due to lack of sufficient evidence linking Zantac use to cancer. These outcomes are crucial in shaping the broader legal landscape of the Zantac lawsuit.
Impact on Veterans and Military Personnel
Veterans and military personnel are a significant group affected by the Zantac lawsuit. Many veterans relied on Zantac for years to manage gastrointestinal issues, often prescribed by VA hospitals. As a result, they represent a large portion of the plaintiffs, with many suffering from cancers linked to NDMA exposure. Their inclusion in the Zantac lawsuit highlights the broader impact on those who served the country.
Legal Developments and Settlements
Timeline of Legal Actions and Court Decisions
The timeline of the Zantac lawsuit is marked by key legal milestones, including the initial discovery of NDMA, FDA warnings, and the filing of thousands of lawsuits. This section outlines the major court decisions and ongoing litigation efforts that continue to shape the Zantac lawsuit landscape.
Multidistrict Litigation (MDL) in Florida
Given the large number of Zantac lawsuits, many have been consolidated into a Multidistrict Litigation (MDL) in the Southern District of Florida. The MDL aims to streamline the legal process by handling pretrial proceedings collectively before returning cases to their original jurisdictions for trial. This consolidation is a critical development in the Zantac lawsuit, potentially leading to broader settlements or judgments.
Recent Settlements by Sanofi and Pfizer
Recently, some pharmaceutical companies involved in the Zantac lawsuit, including Sanofi and Pfizer, have reached settlements with plaintiffs. While the details of these settlements are often confidential, they represent a significant step in resolving some of the claims. These settlements could influence the outcome of other pending cases and the overall trajectory of the Zantac lawsuit.
Who Qualified for a Zantac Lawsuit?
Criteria for Eligibility
To qualify for a Zantac lawsuit, plaintiffs generally need to meet specific criteria. These include a confirmed diagnosis of cancer associated with NDMA exposure, a history of using Zantac, and evidence linking the medication to their illness. Eligibility criteria vary slightly depending on the jurisdiction and the specifics of each case.
Types of Cancer and Health Issues Covered
The Zantac lawsuit primarily covers cancers that have been scientifically linked to NDMA exposure, such as bladder, stomach, and liver cancers. However, some cases also involve other health issues, like PPH and Crohn’s Disease, which plaintiffs claim were exacerbated by Zantac use. Understanding the types of conditions covered is essential for those considering joining the Zantac lawsuit.
How to Determine Eligibility and Next Steps
Potential plaintiffs can determine their eligibility by consulting with a legal expert specializing in pharmaceutical litigation. These lawyers can review medical records, usage history, and other factors to assess the strength of a potential case. For those who qualify, the next steps often involve gathering evidence, filing a claim, and joining the Zantac lawsuit, either individually or as part of an MDL.

Understanding Zantac Litigation
Difference Between Individual Lawsuits and Class-Action
The Zantac lawsuit landscape includes both individual lawsuits and class-action suits. Individual lawsuits allow plaintiffs to pursue compensation based on their specific circumstances, while class-action suits consolidate many claims into one legal action. Understanding the differences can help plaintiffs decide which legal avenue best suits their situation.
Role of Lawyers and Legal Representation
Legal representation is crucial in the Zantac lawsuit, as experienced lawyers can navigate the complexities of pharmaceutical litigation. They assist plaintiffs in building a strong case, negotiating settlements, and ensuring that their rights are protected throughout the legal process. Choosing the right lawyer is a critical step in pursuing a Zantac lawsuit.
What Plaintiffs Need to Know About the Legal Process
The legal process for the Zantac lawsuit can be lengthy and complicated, involving multiple stages such as filing a claim, discovery, pretrial motions, and potentially a trial. Plaintiffs should be prepared for the time commitment and understand the possible outcomes, including settlements or court judgments. Staying informed and engaged in the process is key to a successful outcome.
Current Status of Zantac Lawsuits
Latest Updates on Pending Cases
As of now, the Zantac lawsuit continues to evolve, with new cases being filed and existing ones moving through the court system. Recent updates include ongoing trials, settlements, and decisions in the MDL. Staying informed about these developments is crucial for those involved or considering joining the Zantac lawsuit.
Future Outlook for Zantac Litigation
The future of the Zantac lawsuit remains uncertain, with potential for further settlements, additional lawsuits, and possibly new revelations about the drug’s safety. Legal experts predict that the litigation could continue for years, with significant implications for both plaintiffs and the pharmaceutical industry. Understanding the future outlook can help plaintiffs prepare for what lies ahead.
Resources for Affected Individuals
For those affected by the Zantac lawsuit, numerous resources are available, including legal assistance, support groups, and medical information. These resources can provide guidance on navigating the legal process, managing health concerns, and connecting with others in similar situations. Accessing these resources is an important step in dealing with the impact of Zantac use.

Conclusion
The Zantac lawsuit underscores the critical importance of holding pharmaceutical companies accountable for the safety of their products. The discovery of NDMA contamination in Zantac has led to widespread health concerns and legal actions, impacting thousands of individuals. If you or a loved one have taken Zantac and developed cancer or other serious health conditions, it’s crucial to explore your legal options. Don’t wait for further developments—seek the justice and compensation you deserve. Contact a legal professional today to discuss your case and take the first step toward securing your future.





