Introduction
Picture this: you’re in your garden, spraying away weeds to keep your plants healthy. You’re using glyphosate, a popular herbicide that has been a trusted tool for many. However, concerns about glyphosate health risks have been growing louder recently.
Once considered a gardener’s best friend, glyphosate is now under intense scrutiny due to its potential health risks. From cancer concerns to ongoing lawsuits, the story of glyphosate health risks is both important and alarming. In this blog, we’ll dive into the real dangers associated with glyphosate, explore the legal battles surrounding it, and discuss what you need to know to protect yourself and your loved ones. Let’s uncover the truth about glyphosate health risks and the impact of Roundup.
Table of Contents
What Is Glyphosate?
Glyphosate is a widely used herbicide designed to control unwanted plants and grasses, regulate plant growth, prepare crops for harvest, and aid in fruit ripening. As a nonselective herbicide, glyphosate targets and kills most plants it comes into contact with by inhibiting the production of specific proteins essential for plant growth.
Since its introduction in the U.S. in 1974, glyphosate has become one of the most commonly used herbicides. It finds application across a range of environments, including lawns, gardens, forests, and agricultural fields.
Uses of Glyphosate Herbicide
Glyphosate serves various purposes and is utilized in numerous settings, from residential gardens to large-scale agricultural operations. Farmers frequently apply it during food production processes.
Here are some common uses of glyphosate:
- Fruit and Vegetable Crops: Applied to manage weed growth around edible crops.
- Glyphosate-Resistant Crops: Used on genetically modified crops such as canola, corn, cotton, soybeans, sugar beets, and wheat, which are engineered to withstand glyphosate’s effects while eliminating surrounding weeds.
- Plantings and Lawns: Employed to maintain lawns, greenhouses, and various plantings.
- Aquatic and Forest Areas: Certain glyphosate products are suitable for managing vegetation in or near water bodies like ponds and streams, as well as clearing land in forests for tree planting and weed control, particularly for young trees.
Glyphosate’s widespread use, especially on crops engineered to be resistant to it, underscores its importance in modern agriculture and land management practices.
Overview of Glyphosate Health Risks and Roundup Exposure
Glyphosate, the active ingredient in the widely used herbicide Roundup, has been a staple in agriculture, lawn care, and gardening for decades. Known for its effectiveness in killing a broad range of weeds while sparing crops, Roundup quickly became a go-to solution for farmers, gardeners, and homeowners alike. However, growing concerns about its safety have sparked a heated debate and led to numerous lawsuits.
Health Risks Associated with Glyphosate Exposure
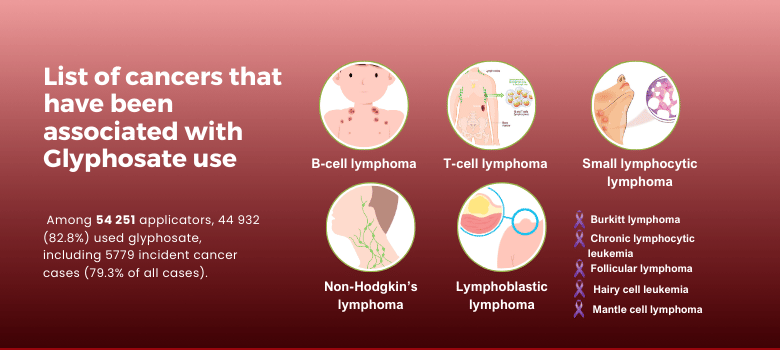
Glyphosate exposure has been linked to several serious health issues, most notably cancer. Studies have shown that glyphosate may increase the risk of developing Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL) and other cancers. Victims of glyphosate exposure often face significant physical, emotional, and financial challenges, with cancer treatments being both costly and physically debilitating.
Background on Roundup Weed Killer
Discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970, glyphosate was introduced to the market in 1976 under the brand name Roundup. Monsanto promoted Roundup as a safe and environmentally friendly herbicide, which contributed to its widespread adoption. By the mid-1990s, Monsanto introduced “Roundup Ready” genetically modified crops resistant to glyphosate, further cementing Roundup’s dominance.
Despite its widespread use, concerns about glyphosate’s safety have arisen. In 2015, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified glyphosate as a “probable human carcinogen,” citing limited evidence in humans but sufficient evidence in animals. This classification has led to numerous legal actions against Monsanto, now owned by Bayer AG.
Scientific Research on Glyphosate Health Risks
Research on glyphosate’s health risks is ongoing and has produced mixed findings. The IARC’s 2015 classification of glyphosate as a probable carcinogen contrasts with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) stance, which maintains that glyphosate is unlikely to cause cancer in humans. The EPA’s evaluation focused on extensive regulatory studies, while the IARC considered a broader range of research, including studies on glyphosate’s primary metabolite, AMPA.

Health Conditions Linked to Glyphosate Exposure
- Cancer: Glyphosate exposure has been linked to various types of cancer, including:
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL): Research indicates a 41% increased risk of NHL due to glyphosate exposure.
- Leukemia: Animal studies show that glyphosate can induce leukemia.
- Multiple Myeloma: Glyphosate exposure has been found to accelerate the progression of multiple myeloma in rats.
- Reproductive Issues: Studies suggest glyphosate exposure may affect reproductive health and fetal development, potentially leading to fertility issues.
- Nervous System Disruptions: Glyphosate may cause neurotoxic effects, disrupting normal neuronal growth and function.
- Gastrointestinal Effects: Long-term exposure has been linked to gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea and other digestive issues.
- Developmental Effects: Prenatal exposure to glyphosate may lead to developmental problems, such as low birth weight.
- Hepatic and Renal Effects: Animal studies have indicated that glyphosate exposure can cause liver damage and kidney impairment.
Roundup Lawsuits and Settlements
Thousands of lawsuits have been filed against Monsanto and Bayer AG, with over $11 billion paid in settlements. Notable cases include:
- A $2.25 billion award in January 2024.
- A $289 million verdict (later reduced) in San Francisco.
- An $80 million settlement in March 2019.
- A $175 million award in October 2023.
While many cases have been settled, thousands of lawsuits remain pending, and new cases continue to be filed. The Roundup MDL 2741, presided over by Judge Vince Chhabria, consolidates many of these cases.
The Role of Roundup Lawyers
Roundup lawyers play a crucial role in representing victims of glyphosate exposure. Their responsibilities include:
- Case Evaluation: Assessing the strength of potential cases.
- Filing Lawsuits: Handling the legal paperwork and filing lawsuits.
- Gathering Evidence: Collecting medical records, expert opinions, and other supporting documents.
- Negotiating Settlements: Working with the manufacturer’s legal team to reach fair settlements.
- Court Representation: Representing clients in court if necessary.

Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice
If you or a loved one has been exposed to glyphosate and developed health problems, it is essential to stay informed about the ongoing litigation. Consult with reputable law firms experienced in handling Roundup cases to understand your legal options. Ensure you seek medical attention and keep thorough documentation related to your exposure and treatment.
For more information or to find out if you qualify for a Roundup lawsuit, contact a Roundup lawyer for a free consultation.





